V současné době existuje mnoho příruček, učebnic a internetových stránek, které radí, jak psát obchodní dopisy. Mnoho studentů se v tomto moři informací utápí a nakonec nevědí, co je tedy správně. Uvádím proto jen omezené množství příkladů. Pro hloubavé studenty pak přidávám odkazy na další materiály.
I)
Letters and emails – general points about their structure, style and content
The layout and persentation of your business letters and emails are very important – it speaks about the competence and professionalism of the person who has written it and the organization this person works for. Only clear and effective correspondence can help to create sound and efficient business.
Example:
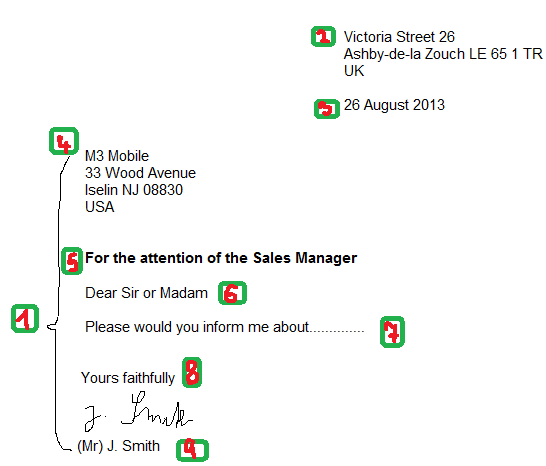
1) Styles or Format of Business Letters
In the UK the blocked style is the most widely used format nowadays. In this style each line starts directly below the one above (see http://www.austinschools.org/campus/small/latest_news/keyboarding/directions/BlockStyleFormat.html). However, business letters may be written in many other styles (see http://yodi-adhari.blogspot.cz/2012/11/styles-format-of-business-letter.html).
2) Sender´s address
The sender’s address is written at the top of the page, unless the letter is written on letterhead. It is placed in the top right-hand corner, but it is also acceptable to place it in the top left-hand corner.
3) Date
The date is directly below the sender´s address and it is separated from it by a space. Be careful with the month in the date! Don´t write it in figures – there is a difference between British and American English.
The sequence in the UK : DAY-MONTH-YEAR |
The sequence in the USA: MONTH-DAY-YEAR |
4) Inside address
It is the name of the person (if you know it) and the address of the company the letter is sent to (just like the one you put on the outside of the envelope).
5) Attention line
It is a line of text (usually positioned above the salutation) denoting the intended recipient within an organization (in case you don’t know the specific name of the addressee).
6) Salutation
A) When the writer knows the name of the person – the salutation will be: Dear Mr, Mrs, Miss or Ms + surname (e.g. Dear Mr Brown).
B) When the writer does not know the name – there are the following possibilities:
British English
| A letter to a man | Dear Sir/Sirs |
| A letter to a woman | Dear Madam |
| The gender is unknown | Dear Sir or Madam |
American English
| A letter to a man | Gentlemen |
| A letter to a woman | Ladies |
| The gender is unknown | Ladies and Gentlemen/ To whom it may concern |
C) Business associates often call each other by their first names. In this case, the addressee can be saluted as follows: Dear Peter, Dear Jane.
It is standard to use a colon (:) in North America after the salutation and a comma (,) in the UK. However, a comma is optional – it is also possible to use no punctuation mark at all.
7) Body of the letter
It’s the main part of the business letter. Regardless of format, skip a line between paragraphs.
Examples of opening lines:
| With reference to your letter of 26 August, I… |
| In reply to your letter of 27 September, … |
| After having seen your advertisement in … , I would like … . |
| Thank you for your letter regarding …. |
| I am writing to enquire about … . |
Examples of closing lines:
| If you require any further information, feel free to contact me. |
| Once again, I apologise for any inconvenience. |
| I look forward to hearing from you/ to your reply. |
| We are looking forward to a successful working relationship in the future. |
| Thank you for your attention to the request. |
8) Professional letter closings
If you do not use a comma or colon in your salutation, leave out the comma after the closing phrase as well.
A) When you know the recipient’s name, close your letter: Yours sincerely.
B) When the recipient’s name is unknown to you (the letter begins Dear Sir/Sirs/Madam/Sir or Madam) – the complimentary close is: Yours faithfully.
C) A letter to someone you know well may close with the more informal: Best wishes, Warm/Kind regards, With appreciation, Cordially.
9) Signature
Type your name below your handwritten signature. You can sign with your initials (e.g. P.Brown) or your full name (e.g. Peter Brown). It is good to include your courtesy title (Mr, Mrs, Ms, Miss) – it will help your correspondent to avoid misunderstanding.
You can find some sample letters on the following websites:
http://www.faxcoverdb.com/469/standard-business-letter-format-example/
http://jobsearch.about.com/od/morejobletters/a/jobacceptletter.htm
http://jobsearch.about.com/od/Employeeletters/a/employment-verification-letter.htm
http://jobsearch.about.com/od/Employeeletters/a/interview-rejection-letter.htm
http://www.4hb.com/letters/ltrapoldely.html